Myopia Control
Prevalence:
Currently approximately 30% of the world’s population is nearsighted (Myopic). It is widely projected that by the year 2050 approximately 50% of the world’s population (an estimated 5 billion people) could become myopic.
NeuroRays’ Hypothesis (Abbreviated)
NeuroRays™ believes it has not only identified the root cause of myopia progression but has also invented a non-invasive, optogenetic neuro-light therapy for possibly (one of): preventing myopia from occurring in the first place or slowing, and maybe even stopping the progression of myopia.
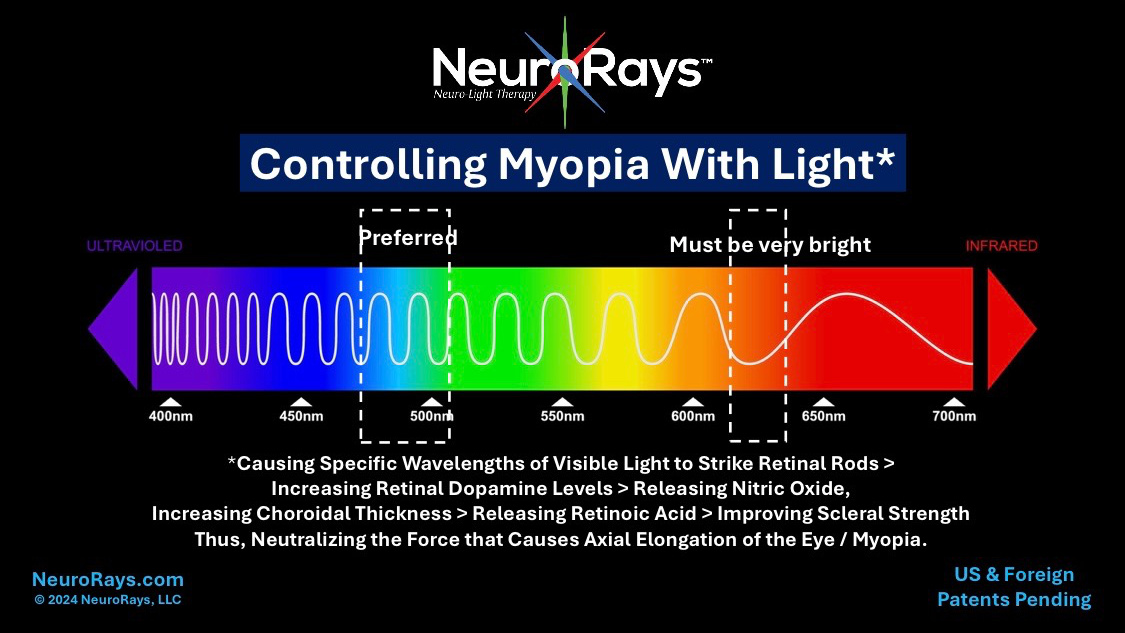
We believe that myopia progression, and possibly even the onset of most myopia, is caused by an imbalance of force of near point accommodative stress and that of the resisting force generated by the eye’s ocular structure. This imbalance we believe is brought on by a deficiency of retinal dopamine, choroidal thinning, hypoxia of the sclera, scleral thinning, which gives way to the elongation of the axial length of the eye. Said another way; When the force caused by accommodative near point stress (is greater than) the offsetting force of the ocular structure of the eye, myopia occurs. By increasing the choroidal thickness of the eye and increasing the health of the sclera (through remodeling), it is possible to increase the offsetting force generated by way of the ocular structure, thus slowing down, or stopping myopia progression.
In addition, we are very suspicious that when eye doctors and / or opticians correct the vision of myopic patients with thin and lite lenses (having Abbe numbers in the low 40s or 30s), these thin and lite lenses may be exacerbating the near point stress, thus increasing myopia once again, causing over time myopia progression. It is our theory that the longitudinal chromatic aberration of these thin and lite lenses generates unrealized near point stress for the wearers, thus possibly leading to myopia progression.
NeuroRays™ Myopia Control Solutions Under Development
DopaLens™
A completely new category of lenses that utilize a clear lens’ inherent chromatic aberration in a positive way to increase retinal dopamine which results in a thicker choroid and a stronger sclera. Both of which increase the strength of the eye’s ocular structure to offset part or all of the force causing axial elongation. DopaLens™ should increase Dopamine in the eye and possibly Dopamine and / or Serotonin in the Brain. Therefore, DopaLens™ can also be worn by patients with other types of dopamine deficiency disorders.
DopaQT™
(QT for Quick Time) A darkened, enhanced version of DopaLens™ that is worn for brief periods of time independent of one’s conventional myopic correcting eyewear or as fit over eyewear in addition one’s conventional eyewear. DopaQT™ delivers the specific wavelengths of light (480nm +/- 30nm) required to produce dopamine in the eye’s retina and possibly Dopamine and /or Serotonin in the Brain. For this reason, DopaQT™ may be able to be worn for minutes in the morning and mid-day to slowdown, and possibly stop myopia progression. DopaQT™ can also be worn by patients with other types of dopamine deficiency disorders.
DopaSun™
The world’s first sunglasses that do not interfere with Dopamine production in the eye and possibly Dopamine and Serotonin production in the Brain. DopaSun™ lenses provide sunlight protection by way of a 30% or lower overall visible light transmission, while transmitting in 50% or more of the light wavelengths within the range of 480nm +/- 30nm that are needed to generate Dopamine in the eye and possibly Dopamine and / or Serotonin in the brain. Children with myopia can safely wear DopaSun™ lenses while potentially slowing their myopia progression. DopaSun™ can also be worn by patients with other types of dopamine deficiency disorders.
DopaTherapy™
The use of blue light (within the wavelength range of 480nm +/- 30nm) to increase retinal dopamine which then directly and indirectly results in a thicker choroid and a stronger sclera. Both of which increase the strength of the eye’s ocular structure thus offsetting part or all of the force causing axial elongation. DopaTherapy™ can be employed prior to a child becoming myopic or after becoming myopia. DopaTherapy™ can also be employed for helping other types of dopamine disorders.
DopaXR™
XR eyewear (AR, MR, VR), that delivers to the eye’s retina the desired wavelengths of light for the purposes of Ocular Photo-Bio-Stimulation. By way of example only, blue light wavelengths of 480nm +/- 30nm for slowing or stopping myopia progression.
DopaEyewear™
Eyewear used to deliver DopaTherapy™ for enhancing the production of Dopamine in the Eye.
